What are the differences and similarities between Transactional and Transformational leadership? Below we examine each leadership style, and then come to some conclusions about how the two styles differ.
Table of Contents
What is Transactional Leadership?
Transactional leadership is a common form of leadership most often found in the middle management level. Transactional leaders are usually directive; they tell their reports what exactly to do and set out expectations and key performance indexes for their reports to meet.
They practice this concept the academics call management-by-exception, where they set work objectives and standards but wait for problems to arise before reacting to them. In other words, transactional leaders are there to maintain the status quo, helping an organization to continue running and fulfilling its mission.
Also, they reward their followers according to their performance and motivating them through these rewards, a concept called contingent reward. These leaders garner more compliance from their followers; people would do as they’re told because its part of their job to do so.
Although this is not considered a ‘high’ form of leadership, it is still a necessary form of leadership to help carry on the mission of an organization. Unfortunately, the reality is that some organizations are so large that no single worker feels that they are contributing much to the overall mission of the organization, and hence transactional leadership is far more effective to lead these people.
This is not a type of leadership that gathers a group of wild and passionate people to do something together, so generally you don’t find this leadership style at the top of volunteer organizations like a church, or in social service organizations.
Characteristics of Transactional Leadership
Transactional leaders often do not get the best from their subordinates. A transactional leader simply exchanges their services for wages and salary with a promise of a bigger bonus.
Most people can become transactional leaders because all they need to do is to work within the policies and procedures of an organization and ensure that their direct reports are producing what is required of them.
It is a ‘lower’ form of leadership, but a necessary one. If you want to become a better leader, you can learn to change your style and learn how you can inspire people and get them to follow you through passion and not because they have to.
Generally speaking, the ideal is to have a visionary or transformational leader at the helm of an organization, while having several managers using the transactional style managing the employees at the middle levels.
Transactional Leadership Examples
Everyday examples of Transactional Leadership include:
- Coaches of athletic teams; leaders that motivate their followers by promoting the reward of winning the game
- Managers of restaurant wait staff; leaders that motivate their followers by promising higher tips and a more comfortable workplace environment if service is delivered at a high level
- Military Drill Sergeants; motivate their followers through fear and punishments to inspire transformation from citizen to soldier
Transactional leadership has a place in many processes and workplaces, and has been a leadership style that has been used by some of the worlds most successful people, for example:
- Norman Schwarzkopf. As a graduate from West Point University, Schwarzkopf was essential in helping revolutionize the coordinated efforts of a United States military in Operation Desert Storm in the 1990s and was also efficient in using the rules and regulations of the US Military to manage strategic efforts on every continent during his time as commander in chief
- Bill Gates. As the founder of one of the worlds most successful companies, Gates was able to inspire results through structure, organization, and by always holding his subordinates to a high standard.
What is Transformational Leadership?
Transformational leadership theory is not really about one style of leadership or another; rather it talks about leadership that makes a positive change to the environment. This environment could mean a small local community or a whole society.
Leaders that transformed the world are many, and all of them have adopted a style that is unique to their culture, and the current needs of their people.
These leaders have changed the way people think; the way people lived; or even the laws of the land that have been deemed unfair or unfavorable. Either way, they have shaped the present world because of their courage and leadership.
Some famous examples of transformational leaders:
- Gandhi, whose non-violent protests have caused the world to think long and hard about racial discrimination.
- William Wilberforce fought to abolish slavery in the UK in the 19th century; and what was deemed lawful and legitimate is now deemed illegal and immoral.
- Mark Zuckerberg changed the face of internet and the way we interacted with one another with the creation of Facebook.
Whether for good or for worse, transformational leaders have truly changed the face of the world with their work.
Characteristics of Transformational Leadership
1. Putting other’s needs before your own
It means that you must be a selfless person. Transformational leaders value the cause they stand for as higher than their personal agendas. They gave up their personal ambition, comfort and luxury in order that the dream they envisioned may come to pass.
Such conviction from these leaders often inspire a huge following and thereby creating power for an idea and a movement. As such, many of the visions of these leaders live on long after their deaths.
2. Challenging the status quo
A transformational leader does not accept the status quo. The leader looks at the current realities and ask what can be better.
They are not satisfied with what they have at the moment. While others will see a status quo and complain about how the status quo is not perfect, a transformational leader courageously challenges it even in the face of opposition.
Many ask, “Why?”; but a transformational leader asks, “Why not?”
3. Inspiring your team
A transformational leader inspires the team with the beauty of the vision. He sees a better future and he articulates this future to the team.
The people who join the transformational leader often do so voluntarily; they are inspired by his vision too and also want to see that vision becoming reality.
4. Being a role model
Being a transformational leader means that you have to have impeccable character standards. While people do follow a vision, people do look at the person that is leading the vision.
If the leader has a hint of hypocrisy or lack of integrity, the leader will lose his credibility and cause a lot of people to walk away. This is because most people join the leader voluntarily, and they will leave if they stop trusting the leader.
The leader needs to be a role model especially in their integrity and their responsibility. The leader must be true to himself and to others and must be ready to be accountable for all actions.
Transformational Leadership Examples
Transformational leadership is based on the concept of inspiring others to act. It is a radically influencing mindset that if implemented successfully, can yield tremendous results. Management theories deduce that there are inherently four traits that are synonymous with all transformational leaders, those being:
- Inspirational Motivation; always seeks to improve the lives of themselves and help people instill motivation in their selves. Transformational leaders are constantly seeking to improve their live in every way possible
- Idealised Influence; transformational leaders are aware of the influence they hold over others and area always thinking of new ways to improve his or herself
- Intellectual Stimulation; through feedback loops, subordinates are stimulated intellectually, and naturally think of ways to accomplish tasks and jobs that will impress the leader
- Individualized Consideration; a transformational leader considers the needs of each subordinate individually and custom tailors his leadership style to fit each person he or she manages.
Many of society’s greatest thinkers and leaders have adopted the transformational mindset. Some of history’s greatest examples include:
- Steve Jobs. Commonly referred to as one of the greatest business leaders of all time, Jobs always inspired success through his pursuit of perfection, simplicity and sophistication and these character traits were always reflected in his employees
- Barack Obama. The first black president in US history inspired results as a charismatic leader who led through values such as compassion and a broad sense of humanity. Obama’s presidency is widely considered a successful one and his transformational leadership techniques are greatly attributed to his success
Similarities Between Transactional and Transformational Leadership
Both Transactional and Transformational leadership styles share many commonalities; they just go about achieving results in different ways. Both techniques involve leaders and followers with a shared purpose to benefit from one another; both approaches are motivational in their approaches; and both leadership styles have inherent goals in mind.
Transactional and Transformational leadership are both answers to the question of how to manage groups of subordinates and use psychological methods that have been developed and tested over time. The two methods are considered to be among the preeminent leadership styles in today’s modern era and are considered highly effective if executed correctly. Research has also shown that both transactional and transformational leadership techniques can yield positive impacts on groups of subordinates.
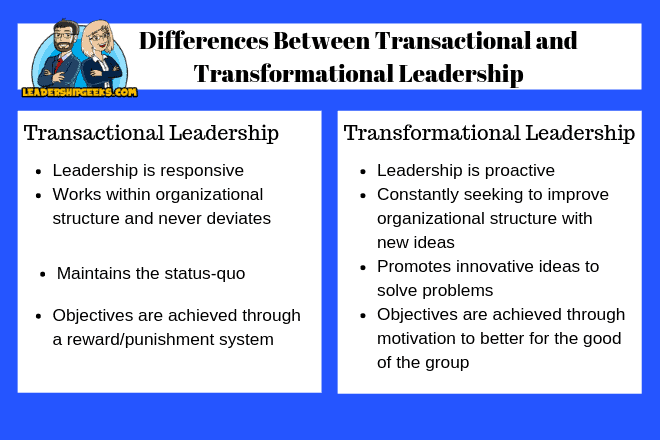
Differences Between Transactional and Transformational Leadership
When it comes to the underlying theories that guide each style, these two leadership techniques are quite different from one another.
Transactional leaders tend to rely more on structure and rules to govern subordinates, while transformational leaders tend to focus on the organization as a whole. To not speak disparagingly of transactional leadership is important here because not every situation calls for transformational leaders.
Transactional leadership is often preferred in many middle management positions at companies in service or manufacturing industries are highly preferred because of the necessity of structure in those respective workplaces. On the other hand, Transformational leadership is more fitting in industries where creativity and abstract thought are needed.
Other fundamental differences between the two leadership approaches consist of traits such as:
Transactional Leadership
- Leadership is responsive
- Works within organizational structure and never deviates
- Maintains the status-quo
- Objectives are achieved through a reward/punishment system
Transformational Leadership
- Leadership is proactive
- Constantly seeking to improve organizational structure with new ideas
- Promotes innovative ideas to solve problems
- Objectives are achieved through motivation to better for the good of the group